You can read our most essential coverage of the coronavirus/covid-19 outbreak for free, and also sign up for our coronavirus newsletter. But please consider subscribing to support our nonprofit journalism.
The state’s five other “indicators” for modifying the rules include:
- ensuring hospitals have the capacity to handle additional surges in covid-19 cases;
- putting protections in place to prevent infections among high risk groups, such as the elderly populations in nursing homes;
- requiring schools, child care facilities and businesses to ensure their students, employees and customers can maintain safe distances from one another;
- setting up systems to develop and deliver necessary therapeutics;
- and creating clear guidelines on when regions will need to reinstate stricter measures.
Newsom didn’t spell out specific metrics for achieving most of these benchmarks during his press conference on Tuesday. But he did say that the state will need to build a contact tracing team that will number in the thousands, in part by relying on volunteer organizations like AmericaCorps and Cal Volunteers.
Mark Ghaly, secretary of California’s Health and Human Services Agency, added that the state will need be able to perform tens of thousands of tests a day for those potentially infected–a goal the state may achieve in “the next couple weeks”–while also ramping up antibody testing that indicates if people were previously infected.
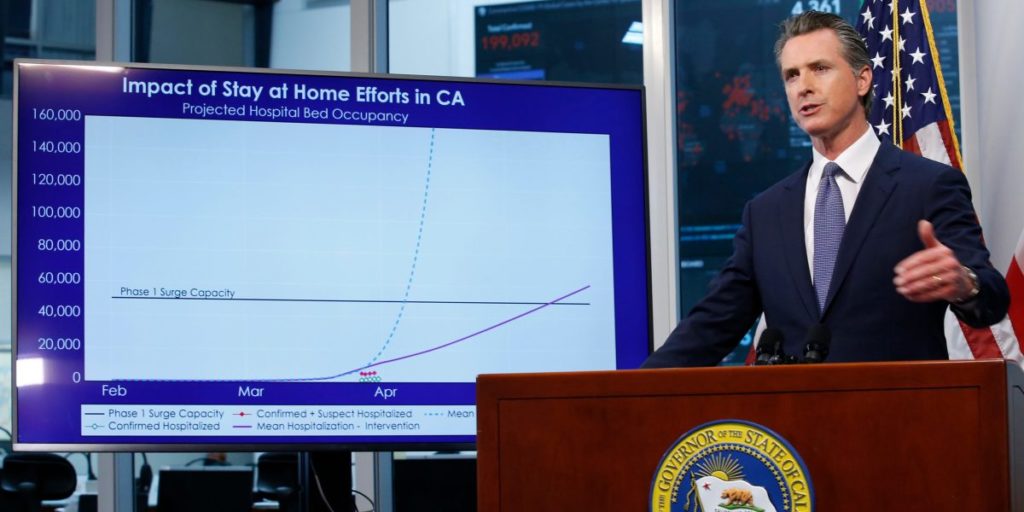
Newsom stressed it’s too early to provide a date for ending the shelter-in-place rules. But he did say that if the disease’s hospitalization and intensive care unit rates decline for the next two weeks and the measures above are largely put in place, he may be able to address such a question at the beginning of May.
“Let’s not make the mistake of pulling the plug too early,” he said. “I don’t want to make a political decision that puts lives at risk.”
He also stressed that local officials will be deeply involved in making these determinations at the city and county level.
California took some of the country’s earliest and most aggressive actions to slow the outbreak, enacting shelter-in-place measures on March 19. The efforts seem to have succeeded in flattening the curve of the disease, and put the state in a position where it could be among the first in the US to consider partially reopening. California’s guidelines may influence other regions considering their own plans to ease restrictions.
On Monday, Newsom and the governors of Oregon and Washington announced the formation of a Western States Pact, through which they agreed to act “in close coordination and collaboration to ensure the virus can never spread wildly in our communities.” Similarly, the East Coast governors of Connecticut, Delaware, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, and Rhode Island agreed to set up a joint committee of experts and officials to guide decisions on easing restrictions.
States have had to take the lead in managing public responses throughout the outbreak, from building up testing capabilities to securing necessary medical equipment, amid cascading federal failures. President Trump, eager to kickstart the economy as soon as possible, shot back in comments to reporters and on Twitter on Monday that he has authority over such decisions, not governors, setting up potential political battles in the months to come.
Newsom decline to address Trump’s remarks when asked by as reporter, saying only: “We just want to get stuff done.”
California’s guidelines are in line with recommendations that other health experts have recently proposed.
Resolve to Save Lives, an organization that aims to prevent epidemics funded by the Gates Foundation, Chan Zuckerberg Initiative and others charities, recently said that regions should only consider relaxing measures when, among other things: coronavirus cases and deaths decrease for at least 14 days; and the area’s healthcare system has the capacity to deal with a suddenly doubling of cases, including necessary protective equipment, staffing, beds and medical devices.
Newsom also echoed health experts in stressing that people and businesses will need to continue exercising social distancing measures even after stay-at-rule measures are lifted. He said restaurants may need to halve their table numbers, take their patrons’ temperatures at the door, and require waitstaff to wear masks and gloves.
Others have said that particularly vulnerable groups will need to continue isolating themselves, and that everyone should wear masks and remain six feet apart from others when they leave the house. Indeed, “prolonged or intermittent social distancing” measures may be necessary into 2022, to prevent hospitals from being overrun with covid-19 cases, according to a Science paper released on Tuesday.
Newsom stressed that regions will need to remain on alert for early signs of subsequent flareups of the disease and ready to quickly restore stricter measures as needed.
“Normal it will not be, until we have herd immunity or we have a vaccine,” he said.