It struck me the other day, while I was reviewing a client project with one of our SEO analysts, that the old problem of thin content is still an insidious revenue killer for many websites.
Or put another way, until you have content worth ranking, do not be surprised if you don’t rank well.
By way of example, the client, a B2B lead gen site for industrial parts, is receiving 150% more traffic this year compared to last and getting a record number of inquiries. We’re seeing these stellar results after many months of work that focused heavily on fixing thin content — until content was improved, the traffic suffered!
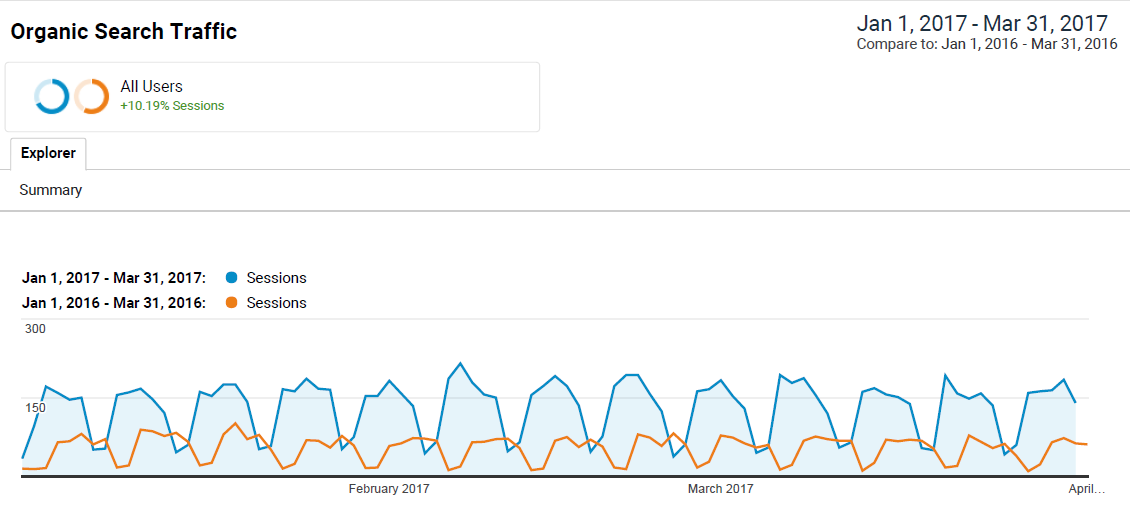
By focusing on improving content quality, our client is seeing 150% more traffic this year compared to last and getting a record number of inquiries. (click to enlarge)
Then looking at some mobile and newer sites reminded me that low-quality or “thin” content remains a serious problem for many websites, whether they know it or not. A majority of sales inquiries are sites with this problem.
SEO changes set the right course for a site, but content improvements give it long-term lift.
Why We’re Still Concerned with Thin Content Long After the 2011 Panda Update
Thin content is not a new search engine optimization issue.
It was February 2011 when Google introduced the first Panda update, which targeted low-quality sites and lowered their rankings. In addition to the algorithmic hits from Panda, countless sites have received manual actions penalizing them for having “Thin content with little or no added value.”
Google has only elevated the importance of quality content since then.
An unconfirmed update in early February and the Google Fred Update on March 7 both targeted low-quality content.
Sites that got hit by Fred included content-driven sites with heavy placement of ads, according to reporting by Barry Schwartz. These sites “saw 50% or higher drops in Google organic traffic overnight.”
Besides the algorithms, Google has an army of people reviewing sites manually for signs of quality. Periodically, Google releases its Quality Rater Guidelines, a document used to train these quality raters to spot low- vs. high-quality content. I unconditionally recommend that you read this entire document from Google!
The search engines clearly intend to keep ratcheting down their quality tolerance. The recent updates and penalties further stress the need for websites to fix thin content without delay.
Solutions for Thin Content
Identifying thin content on a site is crucial to SEO health, yet it’s only the first step.
Once thin content is diagnosed on your site (whether by a Google manual action notice or through an SEO audit), you need a strategic plan for fixing it. And if you’re uncertain, then your content is probably low quality, too terse, or likely both.
The trick is knowing WHICH strategy is right to fix your unique situation.
The solution has to address your site’s situation uniquely, taking into consideration the scope of the problem AND the resources available to you to do the work.
Remove or Improve?
Site owners often react to the news that their sites have many thin content pages with a surgical approach: Cut it all out!
Removing or no-indexing low-value pages can fix thin content problems some of the time, enabling a site to get back on its feet and start regaining lost rankings with minimal time and effort. For instance, Marie Haynes cites one Panda-penalized site that recovered by removing a forum it had hosted, accounting for several thousand low-quality posts that were separate enough from the main site content to be easily detached.
However, removing content can have a negative SEO effect instead. Cutting off whole sections of a site at once could amputate the legs the website needs to stand on, from an SEO perspective.
Another approach is to simply elevate the quality and depth of the content. It is hard to be a “subject matter expert” in only a few words. And if your content is written poorly, then you gain no love from others — the kiss of death for content.
We prefer this latter approach (as does Google, per Gary Illyes’s tweet below), but we use both at the same time quite often.
@Marie_Haynes Thin content: make it better, make it … thick, and ADD more highQ stuff. @jenstar @shendison
— Gary Illyes ᕕ( ᐛ )ᕗ (@methode) October 7, 2015
If the pages hurting your search engine rankings (for being low quality) are also the ones supporting your keyword relevance (for having keyword-containing bulk content), then you’re stuck. You have little choice but to keep the content, improve its quality, and perhaps add more content readers will appreciate.
Finding a Way to Improve Thin Content — Affordably
For this client’s site, we took the content-improvement approach.
The types of thin content we found on their website included:
- Product pages with minimal text (just one or two sentences with a few bullets)
- Pages whose content had been scraped and indexed on many third-party sites
- Image alt attributes lacking text and/or keywords
- Autogenerated title and meta description tags that often lacked targeted keywords
Your site may have similar issues, or may contain other types of thin content. Google’s support topic on thin content lists these common forms:
- Automatically generated content
- Thin affiliate pages
- Content from other sources (example: scraped content or low-quality guest blog posts)
- Doorway pages
Fixing these content problems may involve any or all of the following:
- Removing pages or no-indexing them
- Reducing the number of ads
- Adding at least a few sentences of original text (on filter-category pages, for example)
- Inserting relevant content from a database (in small doses)
- Revising title and meta tags to be unique and contain appropriate page keywords
- Adding original text in image alt attributes and captions
- Rewriting the page entirely
Our client’s site contained a manageable number of pages (less than 500), so we started chipping away.
The SEO analyst first clarified the silo structure of the site, and then prioritized pages for revision starting with the top-level pages for each silo. In batches of 10 or so at a time, pages were rewritten and reviewed, passing back and forth between the client and the BCI analyst. Important products got brand-new full-page descriptions. Information pages were rewritten with thorough explanations. In all, we fattened up about half of the site’s pages.
The strategy worked. Among the SEO services we provided to this client, by far the higher quality content is yielding the biggest wins. The search engines and site visitors are eating it up, with vastly improved rankings, traffic and leads.

Why Your Thin Content Solution Must Be Your Own
If you have an enterprise site with millions of pages, or an ecommerce site with thousands of products, you might be thinking this approach would never work for you.
And you’d be right!
It’s often simply impossible to rewrite each individual page manually on a large website. Yet quality content is a non-negotiable for SEO. Even large sites have to find a way to fatten up or remove their thin content.
Maintaining quality content requires an ongoing investment to maintain rankings — but each site’s specific strategy has to be practical and affordable to implement.
A Prioritized Approach
First, we look for what’s causing the thin content. A template might be producing non-unique meta tags, for instance. The business may be duplicating pages on other domains. A CMS might be building empty or duplicate pages. Whatever the issues are, we try to identify them early and stop the bleeding.
Next, we prioritize which pages to tackle first. It’s worth the effort to hand-edit content on the most important pages of even the largest sites. This priority list should include the home page, the top-level landing page(s) per silo, as well as the most trafficked and highest-ROI product pages. Putting creative energy into making these pages unique and high quality will pay huge SEO dividends.
It’s also crucial to look at competitors’ sites. Even if your content is technically clean and unique, is it as high quality as theirs? Remember that “thin content” can be a relative term, since Google is going to choose the highest quality results to present to a searcher.
More and more often, we include some sort of content development along with our SEO services. As we found with the industrial parts site, fixing thin content can make a long-term difference.
A parting comment: If nobody would share your content, then it is not good enough.
If your site has thin content or other SEO issues, contact us online or give us a call at 1-866-517-1900.
Editor’s note: An earlier version of this post incorrectly stated that Google quality raters assign manual actions, which is not accurate. Thanks to Barry Schwartz for reporting the error.
