When you say a complete SEO audit, we usually think of it as a week-long process. For smaller websites, it doesn’t have to be.
This 13-step website audit is pretty straightforward, using only the bare minimum SEO audit tools you need.
It’s NOT a full website SEO audit by any means because we are not doing a deep dive into technical SEO. We will zero in on on-site audits, keyword research, and competitor analysis instead.
Not rocket science, but this SEO audit calls for your full, undivided attention if you want to do it as fast as you can without missing key details.
Before we start the ball rolling…
What Is an SEO Audit?
A search engine optimization audit diagnoses the overall health of a website to improve its performance, mainly for organic search ranking purposes.
A full SEO audit often has four components:
- On-page SEO audit
- Off-page SEO audit
- Technical SEO audit
- Competitor analysis and keyword research
Why SEO Audit Is Important
There’s only one end goal why you need an SEO audit — and that is to boost your organic search rankings and eventually drive more traffic and leads…and a lot of money.
That’s all there is to it. If a steady stream of prospects and revenue isn’t for you, you’re free to skip this whole website SEO audit shebang.
SEO Audit Tools Necessary
In this quick SEO audit, I will only use free SEO audit tools. Some of these tools, however, require a premium subscription to take full advantage of their features.
Here are the SEO audit tools you need, in order of appearance:
Feel free to use their alternatives. This is democracy — so whatever floats your boat.
For this basic SEO audit tutorial, my main audit subject is Kyoto Localized, a travel service based in Kyoto, Japan. I will also use a couple of other websites.
SEO Site Audit Coverage
“What is included in an SEO audit?” you might ask.
For this website audit, a few things we will look at:
- Multiple versions of your website
- Non-indexed pages and broken links
- On-page SEO elements
- Load time of your site
- Mobile-friendliness of your site
- Structured data of your pages
- Site architecture
- Ranking for your brand name
- Organic traffic and search rankings
- Backlink profile
- Keywords your competitor is ranking for
- Website content
- Keyword and position tracking
How to Conduct SEO Audit in Less Than 1 Hour
I already said a lot, so let’s dive right in. Here’s how to conduct an SEO audit to boost your organic search rankings:
Step #1 – Find Different Versions of Your Site
The first logical step to take when doing a website SEO audit is to make sure that only one version of your website is accessible.
There are four ways a website URL could show up in the address bar:
- https://domain.com
- https://www.domain.com
- http://domain.com
- http://www.domain.com
To an ordinary person, they might appear the same. To Google, unfortunately, they are four separate websites.
And as separate websites, Google treats them differently. Only one of these should be browsable.
Whether or not your domain uses www, it doesn’t matter. What matters is that the URL should use https protocol—that means the website is categorically labeled “secure.”
SSL-encrypted sites tend to receive a modest ranking boost just because Google prefers secure https pages over http pages.
How do you know that your website has multiple versions?
Go to Google.com and use the site command to audit sites’ individual pages.
For example:
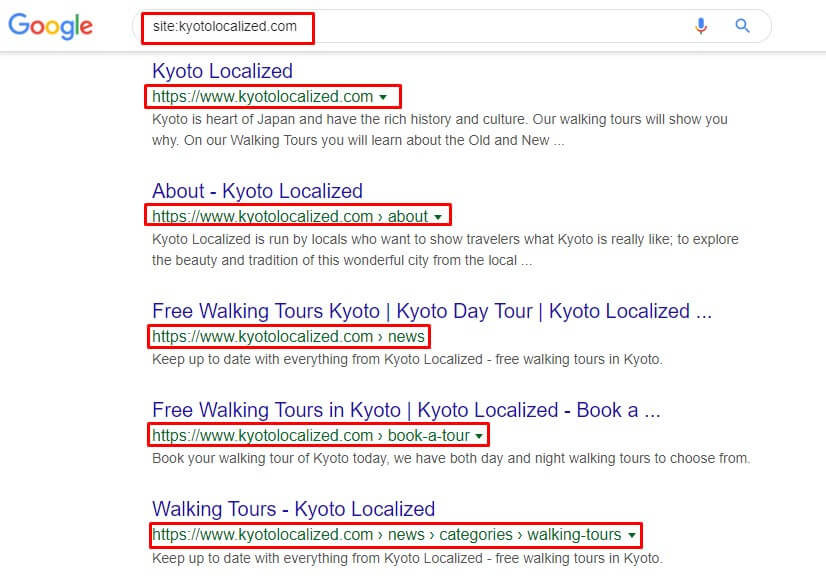
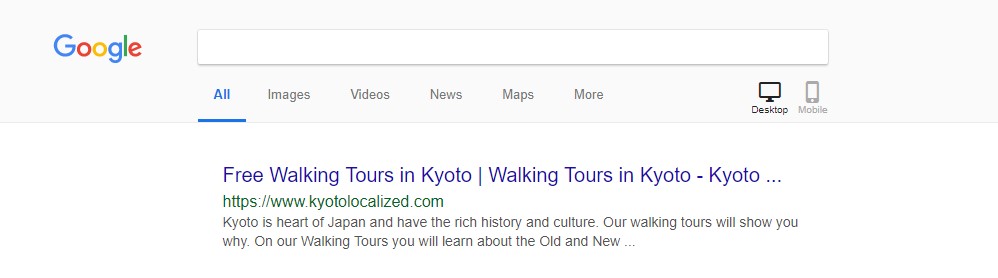
Only https versions appear in the results. Even if I type the http version in the address bar, it automatically redirects to the https version.
In this case, Kyoto Localized is all good.
But what if you find multiple versions of your website?
You need to set up 301 redirects pointing to the https version of the page. Follow Google’s guide on how to set up 301 redirects.
Step #2 – Perform Automatic Website Crawl
The next important step in a website SEO audit is a basic site crawl to find all errors your website has. A website crawl is extremely important because it’s actually the one that sets the tone for the rest of your SEO site audit.
Use Google Search Console to perform some basic site crawl.
Go to Index » Coverage.
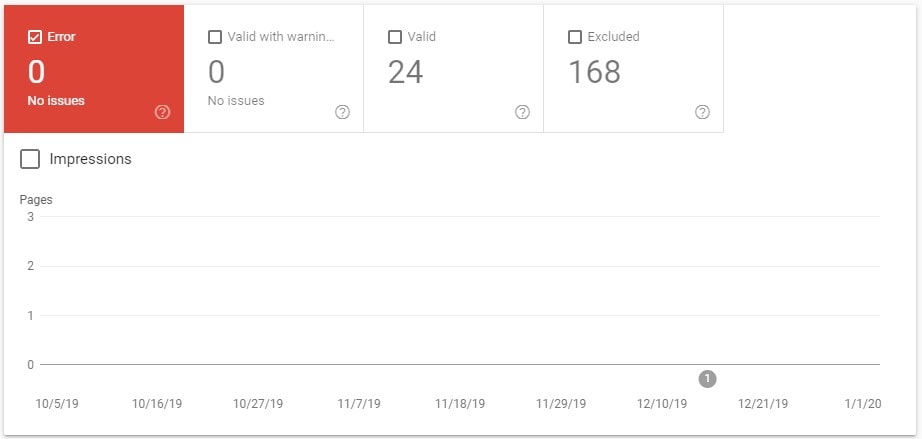
Some issues GSC may report include:
- 404 (page not found)
- Soft 404
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical
- Crawled – not indexed
- And so many others
If you intentionally remove pages (like in the case of dead pages) and GSC still reports them as 404 errors, don’t bother much. It may take some time for GSC to figure out that the pages have been intentionally removed.
With this new niche website, it’s pretty much error-free right now. But you’ve got to double-check since GSC might not have indexed some pages for some reason.
If you are a WordPress user, you can use this free Broken Link Checker plugin to inspect your website and recommend fixes for broken links automatically.
Broken links are bad for SEO. You can fix them by either:
- Replacing the page’s content
- Redirect the page to the closest related existing page
- Leaving the broken page as a 404 as long as it doesn’t have backlinks
Use SEMrush to do a full website crawl quickly and easily.
Create a project. Go to Site Audit » Issues.
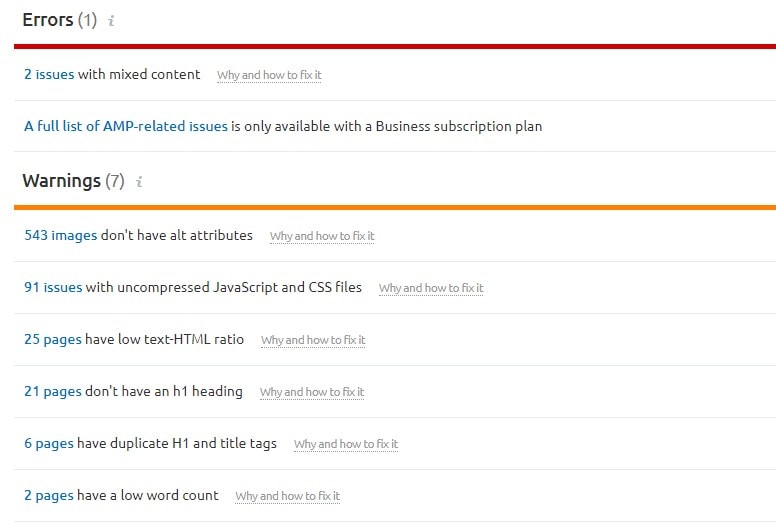
Click on each error and warning to get some recommendations on how to fix it.
Step #3 – Conduct On-Page Audit
Conducting some on-page SEO checks enables you to find low-hanging opportunities to optimize your website for conversions. It’s extremely important because even tiny changes can move the needle.
When doing some basic SEO page audit, look at two characteristics on every page — domain level and page level.
But what if you have hundreds or thousands of pages? Do you need to check and optimize them individually?
Actually, you don’t.
What you can do is to single out the top 10 pages (or more if you want) that brought in the highest amount of organic traffic in the last 6-12 months.
More often than not, these pages are your main navigation pages, category pages, and cornerstone content.
Whether you are looking to push a specific blog post to the top of the search engine results or improve the ranking of a page that targets your target keyword…
When improving your site’s on-page SEO, here are the most important things you should look at:
- URLs
- Keywords
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Header tags
- Body tags
URL
On the domain level, look at your URLs first.
URLs should be short and easy to read yet descriptive. Ideally, no more than 120 characters. The shorter, the better.
It should include your target keyword and describe the page’s content.
In terms of site structure, subfolders are preferred among SEOs over subdomains for ranking reasons. Because they are easier to set up and for search engines and readers to understand.
More about site structure later.
Keywords
If you’re sure about your primary keyword, feel free to skip this. Otherwise, ask yourself:
Are there enough people searching for the keyword you are targeting?
Let’s look at the search volume for “kyoto free walking tour” using SEMrush.

Not a lot, but it’s decent enough for the target market and the size of the business.
The question is — are you using your main target keyword in the most important places?
Let’s start with the home page.
Right-click and then click Page view source.
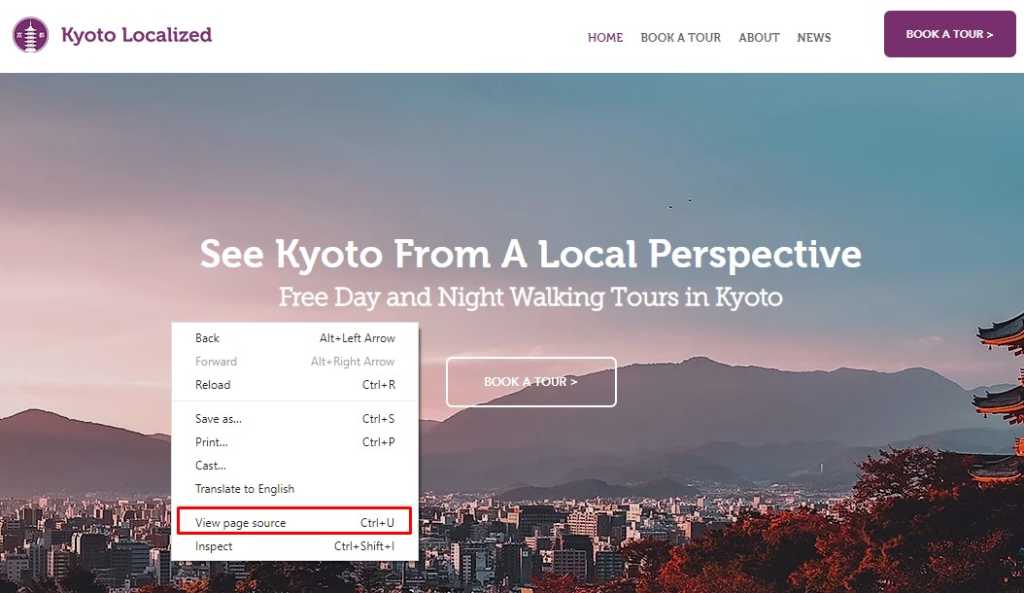
Title Tag
Look for the title tag.
![]()
The meta title tag contains the keywords, but it doesn’t show up in the actual title that appears on the search results.
We need to update that.
Use SERP Simulator to fetch and check a page’s title tag and meta description pixel length for mobile and desktop devices.
A page’s title is the first thing that search engines show in the results, and it’s the first thing that people read. That’s why it remains a strong on-page ranking factor.
It pays to optimize your titles for click-throughs because click-through rate (CTR) is a huge ranking factor nowadays.
A good title is neither too short nor too long. The sweet spot is not over 70 characters. Remember, longer titles get truncated in the search engine results.
Your title should also include your target keyword for that page. Place the keyword near the beginning.
And the title should match the page’s content. Make sure that no title is exactly the same site-wide.
Google Search Console no longer gives HTML improvements that check for duplicate titles on a website. SEMrush does.
Alternatively, you can use Screaming Frog or Moz Pro to check for duplicate issues. Screaming Frog is free for the first 500 URLs.
Meta Descriptions
A meta description doesn’t directly influence search ranking, but it influences CTR, which is a ranking factor.
Though Google automatically pulls out a meta description from the page’s content, it’s important to customize this.
If you are using the Yoast plugin on WordPress or other similar tools, your life would be so much easier.
With Kyoto Localized, the meta description includes its target keywords, a call-to-action, and other relevant keywords. That’s great.
![]()
The problem is, it’s too long that it got truncated.

To optimize a page’s meta description, limit it to only 155 characters with your target keywords included.
Like your page title, your meta description should also be unique and descriptive.
The best meta description communicates your value proposition. If you are in eCommerce, adding your unique selling proposition — such as free delivery, money-back guarantee, or cheapest in the market — can make a huge difference.
HTML Tags
There should be only one H1 tag. Though, Mueller mentioned before that having multiple H1 tags on a page is okay. However, it might confuse your visitors.
Subheaders must also be used accordingly. Make sure an H2 tag is followed by an H3 tag, not H4 or H5 tag.
In Kyoto Localized’s case, it looks good. To improve this, the H1 tag should contain the primary keyword.
In the lower heading tags, there are LSI keywords mentioned, which is good.
In the <body> section, avoid using too many frames if possible. Also, avoid putting too many ads to a point where they overpower your content.
Read this article to get more on-page SEO tips that increase your organic traffic and this article on on-page SEO techniques you should avoid here.
Step #4 – Check Load Time
A site’s loading speed is a ranking factor. No debate — Google confirmed that.
But you would want your website to load fast not just for ranking reasons, but also for smoother user experience and much better conversions.
The average load time of the highest-ranking sites in Google is less than 3 seconds.
Longer than 3 seconds, visitors will consider leaving your site.
Fortunately, there are plenty of free SEO tools that check site speed and give you valuable optimization suggestions.
Using Google’s Pagespeed Insights tool is a good start to test your site’s loading speed for mobile and desktop devices.
Right off the bat, we see that Kyoto Localized badly needs a ton of speed optimization work for both mobile and desktop.
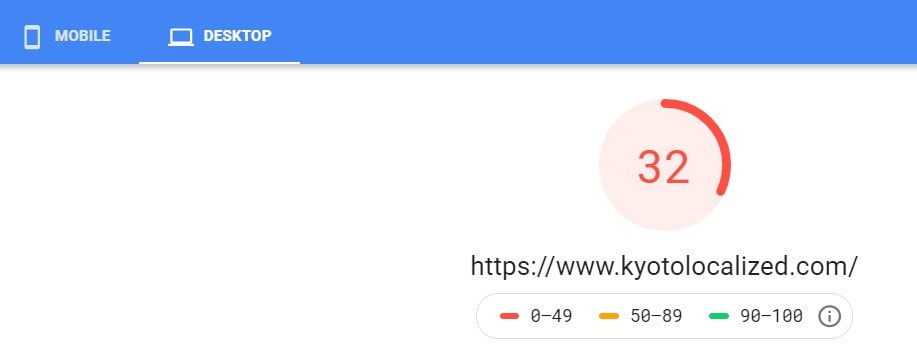
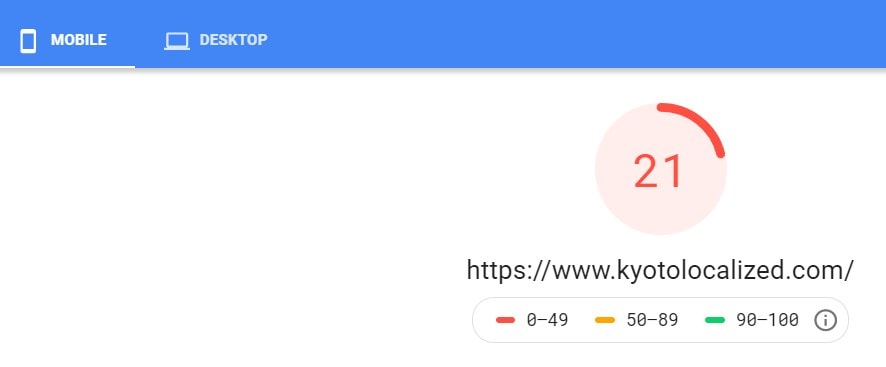
PageSpeed Insights will show its diagnosis as well as opportunities and suggestions you can do to fix HTML code errors and improve your site speed in general.
Test your most important pages as well. If you want an SEO audit tool that allows you to check your site’s pages from top to bottom, Ahrefs, Moz Pro, and SEMrush can do that.
To keep your site from loading like a turtle, here are some SEO best practices to always keep in mind:
- Compress your images. If you are using WordPress, freemium plugins like Imagify and Compress JPEG and PNG images by TinyPNG can automatically optimize your images with limits and options to set some parameters.
- Deactivate unused plugins. Plugins make our lives much easier. But if it’s unnecessary or you’re not using it, might as well remove it.
- Enable browser caching. Browser cache stores some of your site’s data on the visitor’s web browser. So when they come back, your site loads faster.
For more actionable tips on how to speed up your website, check out this guide here.
Step #5 – Do the Mobile-Friendly Test
Is your site mobile-friendly? Mobile SEO is now more important than ever. And it matters a lot.
First, Google prioritizes the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking. Second, 60% of Google searches now come from smartphones and other mobile devices.
Learn more about Google’s mobile-first indexing.
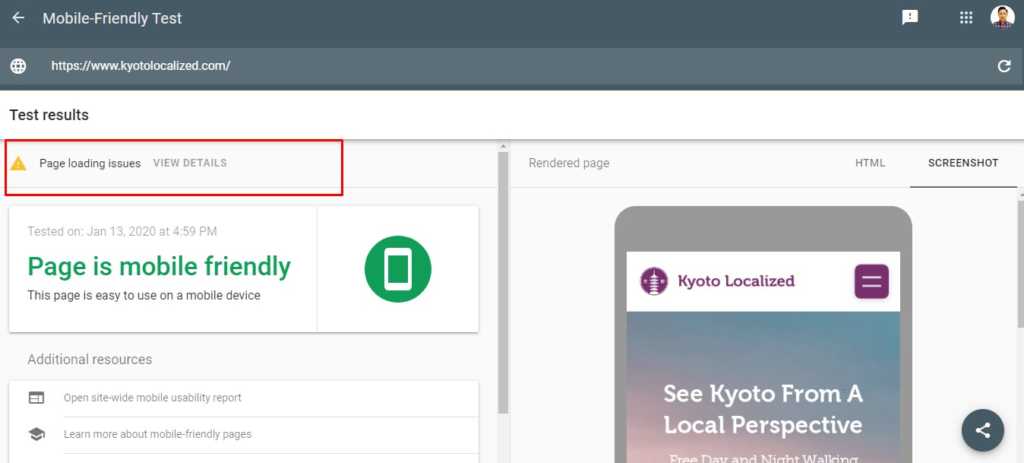
To check if your site is mobile-friendly, use Google’s Mobile-Testing tool.
Kyoto Localized is mobile-friendly, though it has some page loading issues.
Step #6 – Check Structured Data
The next step in this on-site SEO audit is to do an SEO analysis of your website on a deeper level — your structured data.
Google relies on structured data to understand the content of a page. Learn more about Google’s structured data guide here.
On the SERP side, here’s how structured data looks like:

Structured data is beneficial for showing details like star ratings, authors, product pricing, and availability, among other things. You can mark up pretty much any type of content, not just reviews, recipes, or events.
To check a page’s current structured data is in the right shape, use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
Google will tell you if the page has errors. Here’s how to fix Schema markup errors.
In this case, I found no errors so far. You can use the Schema.org plugin on WordPress to mark up details of a page easily.
Step #7 – Check Site Architecture
Both Google and users appreciate a simple, straightforward site architecture.
Because first of all, it’s less complex and more organized. It’s easier for search engine bots to crawl and understand and for readers to navigate around.
And equally important, site architecture allows search engines to know which pages are the most important.
Here’s a good example of a bad site architecture:

And here’s how your site architecture should look like:

Pages closer to the homepage are more important. As much as possible, your deepest pages should be reachable 3 clicks away from the home page.
For an eCommerce site, auditing and fixing the site structure is very important because it directly affects conversions. And it can be a bit complicated to do so because there are lots of product pages.
If your site’s navigation is all over the place, as in beyond comprehension by a regular person, you might have to reach out to a website developer to fix it.
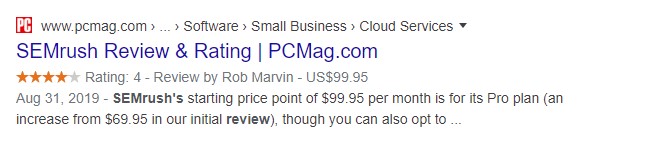
Step #8 – Do Quick Brand Search on Google
Now it’s time to do a quick SEO keyword audit for your brand name to see if you have position 1.
If you are first, all is good. But if not, here are the possible scenarios:
- Your site is fairly new.
- Your brand name is too generic.
- Google thinks another site is more appropriate for your brand name.
Whichever is your case, the best thing to do is to implement some brand and link building strategies. Done right, you should start seeing your site climb up the search rankings in a few months.
If neither of these scenarios applies to you, dig deeper and look for potential penalties.
Use Google Search Console to check for any indication of penalties.
Ideally, your manual actions should look like this:

If you find out you’ve been penalized, make sure to fix all Google penalties.
Step #9 – Analyze Organic Traffic and Search Rankings
A complete site audit is never complete without analyzing organic traffic. Our goal, after all, is to find ways to increase your site’s organic traffic and search ranking.
Since I will be using Google Analytics, I will use my 1-year-old niche site with only two blog content and zero SEO efforts being done…
Open Google Analytics to do this.
Go to Acquisition » All Traffic » Channels.
Click Organic Search.

Then, click Landing Page.
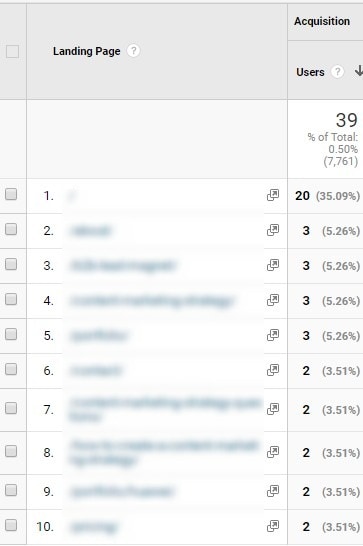
Take note of your top 10 pages because we will make some on-page SEO checks in the next section.
Before that, make sure that your site is treading the right direction by comparing your current year to last year.
Depending on your SEO efforts, your graph might look like it’s increasing, declining, or plateauing.
Also, check your stats in week view to see traffic dips. There are a lot of reasons for dips —a penalty is one of them. Watch out!
Step #10 – Conduct Backlink Audit
Backlinks are still one of the strongest ranking signals.
Brian Dean’s team at Backlinko did a study of 1 million search results and found that backlinks directly affect rankings more than any signals.
But not all backlinks are equal. Let’s do a quick backlink profile audit for your site to find out which ones are bad and which ones are good.
The best SEO audit tools to do an SEO backlink audit are:
In this tutorial, I will use SEMrush.
Enter your homepage into SEMrush’s search bar.

You’ll get an overview of your backlink profile.
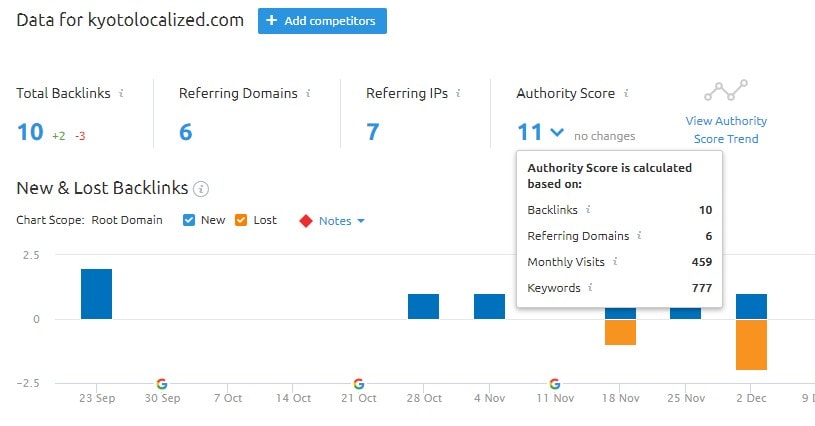
Referring Domains simply means the number of websites that have at least one link pointing to your site.
Authority Score basically tells you how much authority a site has. And the quantity and quality of the backlinks have a HUGE influence on that.
Other tools have their own names for Authority Score. Moz calls it Domain Authority, while Ahrefs calls it Domain Rating.
As you can see, this site needs a lot of link building work to do.
And equally important, you need to look out for toxic links. They’re usually from spammy websites and websites that you don’t want to associate with.
To find toxic links, go to the Anchor section to see the anchor terms that are used to link to your site.
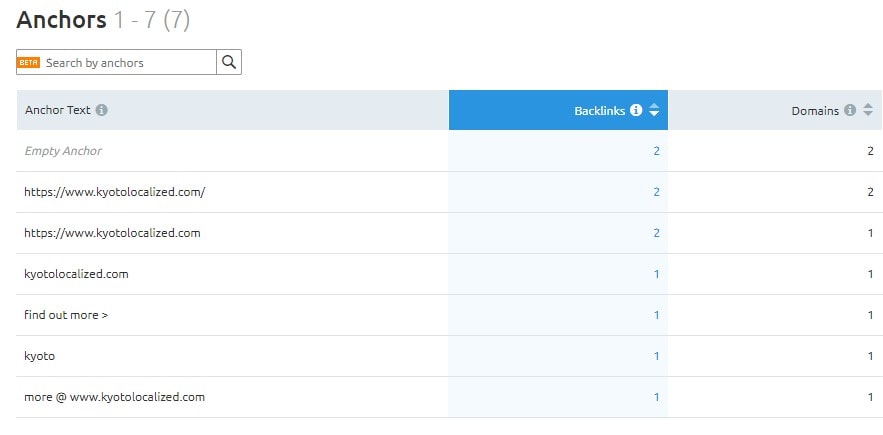
What you want to see are branded anchor terms such as Kyoto Localized and KyotoLocalized.com.
You don’t want to see keyword-rich and spammy anchor terms like travel service, travel company, click here, here, website, etc. These might be toxic backlinks.
To ensure that your backlinks come from valid sites, go to Referring Domains.
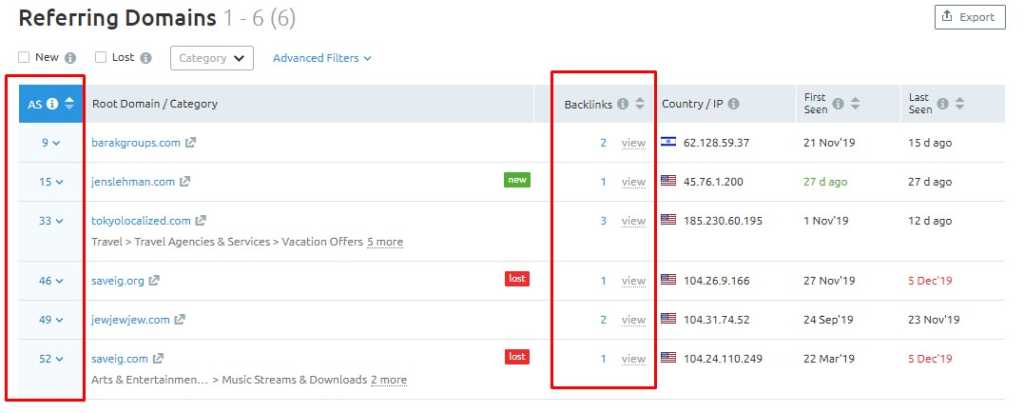
First things first, look at the authority score and the number of backlinks those referring domains have.
Low authority sites with fewer backlinks are often spammy websites. We do not want to associate with those websites, so we will disavow these toxic links.
But before you do so, remember that not all links with low domain authority are spammy or low quality. They may be legit and are helping your site to rank.
Therefore, make sure that the links you’ll disavow are REALLY from shady websites.
Step #11 – Do Competitor Analysis
Any website SEO audit isn’t complete without a competitor website audit.
If you have a tough competition who doesn’t give without a fight, you better up your game.
Just to be clear, we’re not doing a complete website audit of your competitors. We’re just going to keep tabs on your competition’s keywords.
When spying on your competitors, we need to look at two things:
- Keywords your competition ranks for that you’re not
- Keywords your competition ranks for on the first page that you are for on the 2-10 page
Using SEMrush’s Keyword Gap tool, you can easily compare the organic keywords of your site to four of your closest competitors.
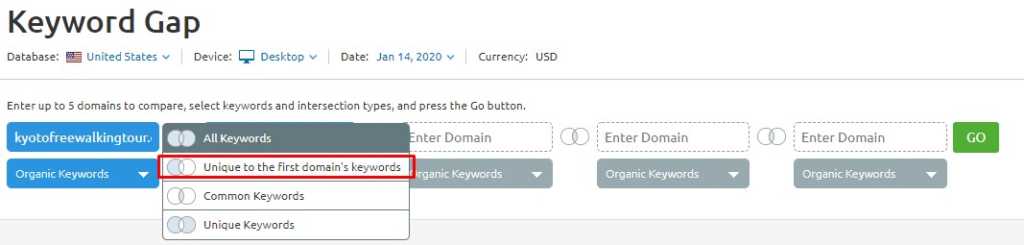
1. Look for Keywords Unique to Your Competitor
Put your top competitor first.
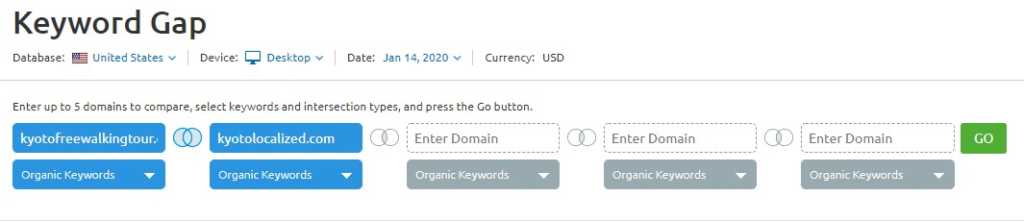
Make sure that you select keywords unique to the first domain’s keywords.
You can export the data into a spreadsheet.
In this case, the competition ranks for 143 keywords that Kyoto Localized hasn’t ranked for.
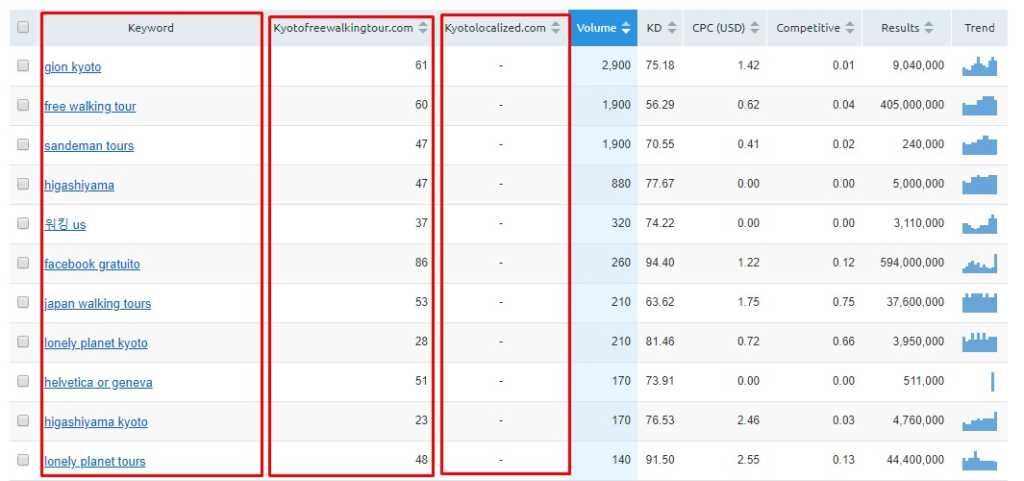
We can then find and export the keywords that matter to the website or business and start building content around those keywords.
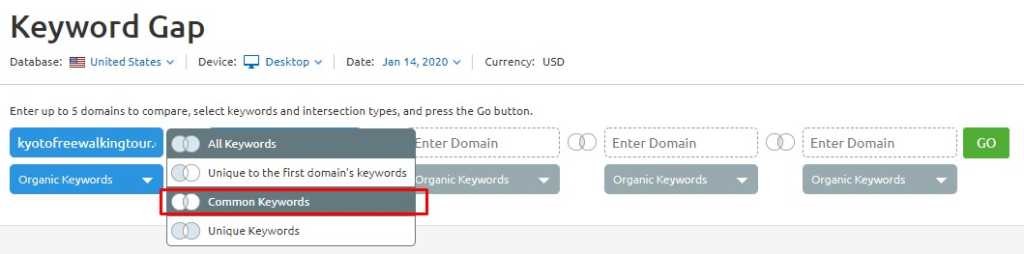
2. Find Keywords Your Competitor Ranks for on 1st Page That You Rank for on 2nd-10th Page
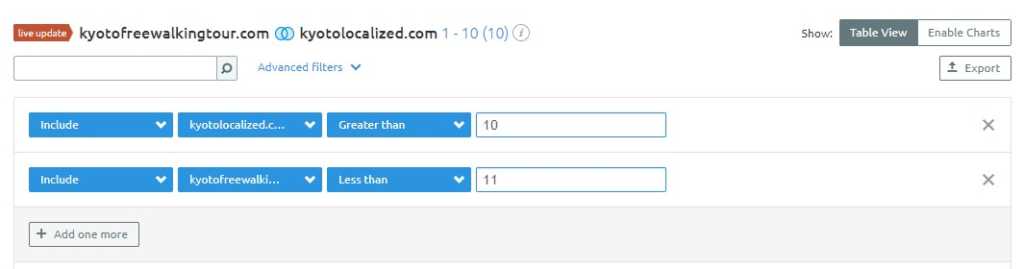
Pick up on the previous process, and change to common keywords.
And then add the following filters.

You get common keywords that both of you rank for, except your competitor is on the first page.

You can use these keyword opportunities to improve your content ranking past the first page.
Take note of these keyword opportunities because you can use them in the following section.
Step #12 – Perform Website Content Audit
Doing an SEO content audit and the next steps can take up a huge chunk of your time. But it will be so worth it if you do it right.
Did you know? Having tons of low-quality thin pages can affect how Google sees your site.
Like with any other content audit for SEO, our goal here is to find low-hanging opportunities to increase your search traffic.
The whole website content audit process may include finding:
- Underperforming content
- Duplicate content
- Thin content
- Keyword-cannibalizing content
- Top-ranking pages (You read it right!)
1. Find Underperforming Content
We categorize pages that haven’t generated much traffic, conversions, or backlinks as underperforming content.
A few ways you can treat underperforming content:
- Update and relaunch it.
- Add visuals, videos, or images.
- Improve the formatting and make it more readable.
- Add more internal links.
- Add more closely related keywords.
- Optimize for featured snippets.
You can use SEMrush to find the backlinks and keywords that your site ranks for.
If you want to look at social shares and evergreen score, BuzzSumo is a nifty tool.
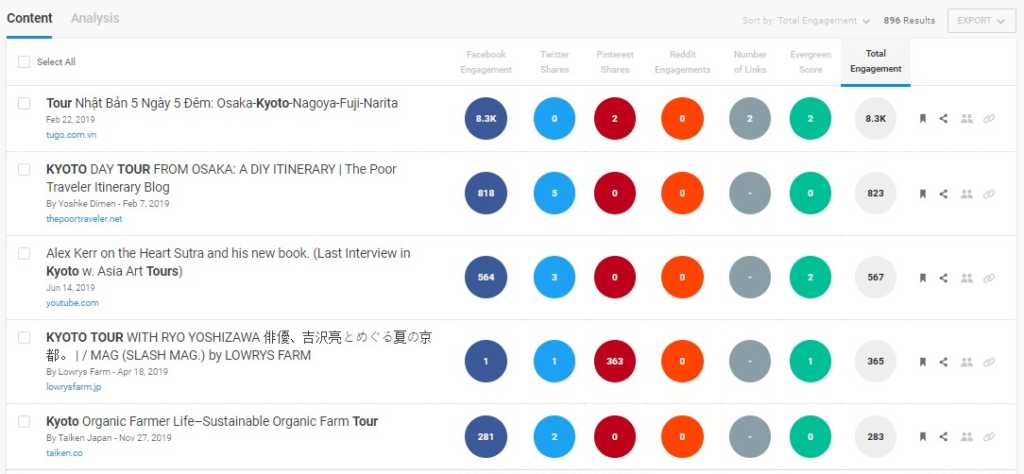
2. Find Duplicate Content
Google abhors unoriginal content.
Flooding your site with duplicate and low-quality content is like cordially inviting Google Panda to raze your site to the ground.
You don’t have to take it literally, but my point is, it’s bad for SEO!
To find duplicate content site-wide…
Let’s use SEMrush’s Site Audit tool.
Go to Site Audit » Project » Issues » Duplicate.

Note that SEMrush’s Duplicate filter includes title tags, content, meta description, heading tags, and versions of your website.
We’ve done checking those things in the previous steps. Our concern right now is duplicate content.
In this case, I can’t find any. If you find duplicate content without canonical, click the issue to see the exact URLs causing the duplicate content and fix them accordingly.
To scour the web for similar content, use Copyscape or Siteliner.

Use Copyscape’s Premium Search to check your site’s individual pages, Batch Search to check multiple pages at once, or Private Index to check your pages against your previous content.
Be wary, though, because these tools may flag down content that is apparently taken from a generic template. It could be affiliate disclosure banners, text disclaimers, privacy policy, and terms and conditions.
In that case, there’s nothing to worry about.
What you should look out for are other websites copying, for instance, your blog posts verbatim.
Duplicate content confuses Google which one’s the original.
To avoid this, make sure that copycats link back to the original content. In case of duplicate content within your website, 301 redirect (with a rel=”canonical” link) the duplicate content to the original.
3. Find Thin Content
Thin pages have little to no written content. This often translates to no value and therefore finds it difficult to rank.
Use a tool like Word Counter to keep your individual pages in check in terms of word count.
A page should have at least 300 words. Otherwise, you need to beef it up or remove it.
Be extra cautious when removing pages. Your first move should be to improve the content.
If you think it’s not worth the time, delete it or be sure to 301 redirect it to a closely related page to maximize link juice.
To find thin content site-wide, go to Site Audit » Project » Issues » Indexability.

Click on the issues to know which pages need revamping.
4. Find Keyword-Cannibalizing Content
Keyword cannibalization happens when two or more pages are gunning for the same target keyword.
Keep your target keyword for each page unique.
If you have keyword-cannibalizing pages, merge them into one post. Alternatively, you can delete the other page and/or 301 redirect it to the canonical page (more authoritative page).
Doing a website crawl lets you know if there are any duplicate keywords. Even Google
Search Console lets you know if you have duplicate keywords.
If you are using SEO tools on WordPress like Yoast, it can warn you if you are going after the same keywords.
5. Find Top-Ranking Pages
And finally, we will find top-ranking pages that are not quite there yet.
If you have posts that already crack the top 10 positions for high-volume keywords, it’s a low-hanging opportunity to boost their rankings.
With a few on-page SEO tweaks, you can push these posts further to the top and drive more traffic.
Let’s use SEMrush to find these pages.

Go to Organic Keywords » Top Organic Keywords.
Filter by the top 10 positions in organic search.

You can filter by search volume as well. In this case, KL focuses on low-volume long-tail keywords.
Take note of the content or URL.
To improve these pages, a few things we can do…
- Update the content, including the images.
- Place more relevant internal links to the pages.
- Add new backlinks to the pages.
- Optimize for the primary keyword.
Step #13 – Track Keywords and Position
You’re basically done here. However, you want to keep abreast of the progress of your website’s SEO.
SEMrush, I believe, is still the best SEO tool to monitor your rankings in the search engine results pages. Read this detailed showdown of the best SEO tools: SEMrush vs Ahrefs vs Moz vs SpyFu.
![]()
With SEMrush’s Position Tracking tool, you can track not just the target keywords that you ask the tool to track, but also the keywords that you are ranking for.
Conclusion
And we’re done! That’s pretty much everything you need to know how to do an SEO audit of your website.
If you are looking to do a forensic SEO audit, you can dedicate another day (or week!) to do that. A full SEO audit usually takes a few days, especially if you have thousands of pages.
By following this instant SEO audit process, I hope you have found a lot of SEO opportunities that may improve your site’s performance in the search rankings.
Got some questions or any other basic SEO auditing tips? Please let me know in the comments!
If you liked this article, please share it on Twitter using the link below:
Related Articles

